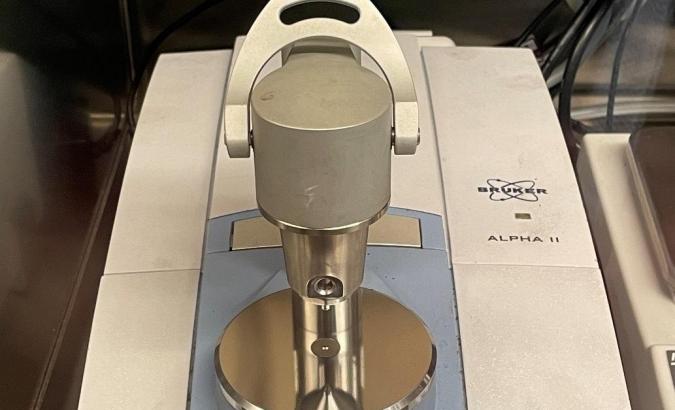
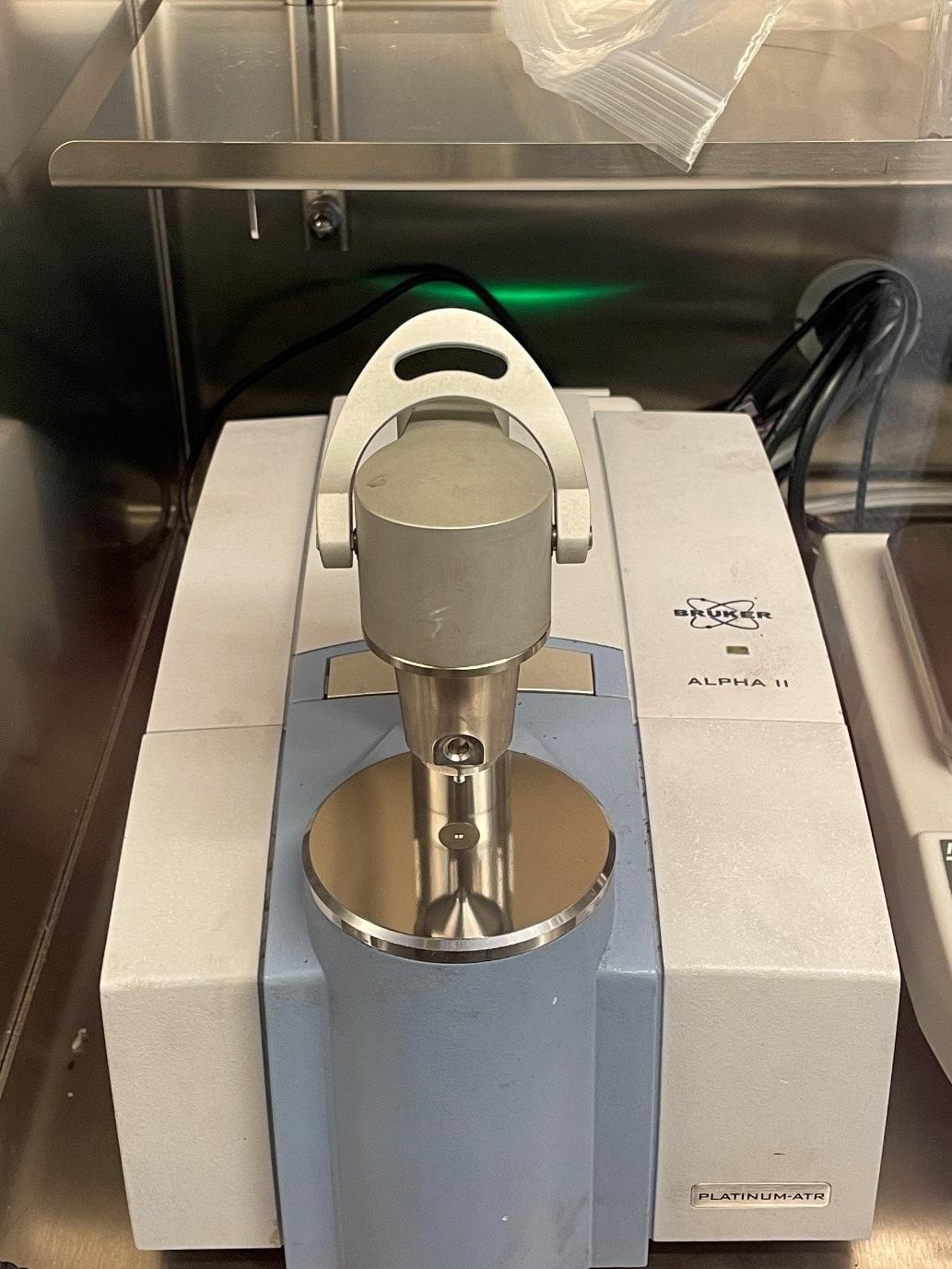
Bruker Alpha
The Alpha is equipped with an ATR module using a diamond aperture for use with powders and solids, looking at spectra range of 4000-400 cm-1 using the Opus software. The Alpha is currently used to look at samples in an Argon environment by being placed in our Mbraun Glovebox.
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is a technique that looks at the molecular structure of a sample by exploiting its characteristics molecular vibrations, with a beam of energy operating in the visible to infrared spectrum and looking at the resultant photon absorption phenomena. The data can be visualized by plotting either absorbance units (a.u.) or percentage transmitted light (%) against the inverse wavelength (wavenumber) used to excite the bond to excite the bond. For a material to be IR active, there must be a dipole moment change during the vibration. The collected data is then processed using Fourier Transform (FT) to display the data in a more logical way for the user. There are multiple pieces of equipment capable of FTIR in Physical Science, either by transmission for gases and thin films or by Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) for solids, powders and liquids.